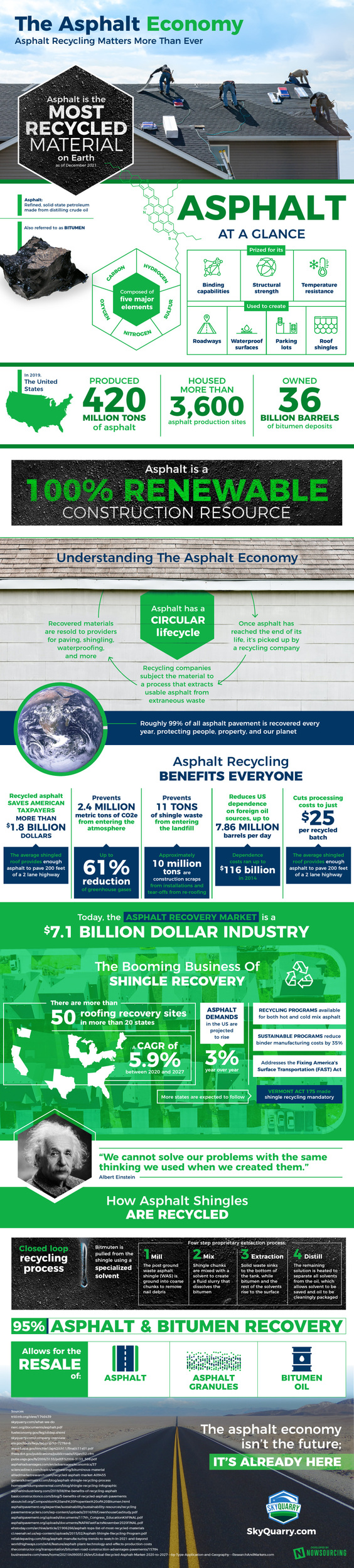
What is asphalt? Considered a very sustainable and 100% renewable material on our planet, asphalt is a material obtained through the distillation of crude oil. Also called bitumen this material is usually composed of oxygen, hydrogen, and carbon. It is a useful construction resource due to its qualities, such as its overall strength and resistance to hot and cold temperatures.
In order to understand the asphalt economy you have to know about asphalt’s life cycle. Asphalt can be reused after going through an extraction process that retrieves good asphalt that can be used again from irrelevant waste. The recovered asphalt is used once again for paving roads, adding roof shingles to houses, and waterproofing surfaces.
Recycling asphalt has a positive impact on various aspects of our lives. Reusing the material can reduce greenhouse gases from entering the air, decrease dependence costs from using outside oil sources, and save U.S. taxpayers billions of dollars. These contributions have also helped the asphalt recovery market reach a value of more than $7 billion.
The shingle recovery market has been gaining momentum with the asphalt recovery market. The market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of almost 6% between 2020 and 2027 while the need for asphalt increases by an estimated 3% each year. In fact, the Vermont Act 175 has required the state to recycle shingles, and there are expectations for this law to be implemented in other states.
How are asphalt shingles properly recycled? The process involves the old asphalt shingle being ground into smaller pieces to remove any extra waste. A solvent is then added to produce a fluid mixture that separates the bitumen and all of the solvents from the oil and other waste particles. Heat aids the extraction process until the solvent can be saved and the oil can be packed separately.
With asphalt being such a versatile material, the asphalt economy has a promising future. Learn more about asphalt recycling in the infographic below:
Source: InvestSkyQuarry.com

